Technical information
The electric charging system on a motorcycle has two parts, the alternator and the regulator rectifier. The alternator (one-phase or three-phase) gets power from the engine and produces an alternating current (AC). The regulator rectifier transforms this alternating current to direct current (DC) and controls the output voltage to a steady 14.4V level, wich is needed for the battery to be charged. The output voltage must always be 14.4V in all driving conditions and engine speed.
Charging system check
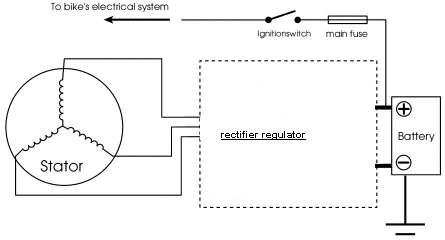
To check the charging system of our motorcycle, we need a digital voltmeter. First, we select the 0-20V selection and connect it to the battery leads. The reading must be 13.5-14.5V with engine at 2500 RPM and the lights on. If the voltage is higher than 15.2V, the regulator rectifier is damaged and needs replacement.
A lower voltage than 13.5V has the following causes:
- a) bad or loose connections of the cables and plugs
- b) the alternator is damaged
- c) The regulator rectifier is damaged
- Check the connections, we check the cables and the plugs that connect the rectifier with the battery and the alternator. We must also check the battery leads for bad connection.
- Check the alternator, we check each phase coil's resistance. The resistance of each coil must be 0.5-2 when the scale of X200 ohms is selected.
- Next, check each coil with ground. We select the scale X2M and the resistance measured must be maximum. If any of the conditions are not met, the alternator is damaged and needs replacement.
- Finaly, If the cables connections and alternator do not have any problems then the problem is the rectifier wich must be replaced.
Do not hesitate to contact us, if you need more information.

